Takeaways from the Regulations on Countering Foreign Sanctions


New Regulations on Countering Foreign Sanctions are adopted to strengthen the legal framework of countermeasures.
By丨Guoxun Zhang, Zhiguo Yu, Jenny Pan, Tristan Zhang
Background
On March 23, 2025, the State Council adopted the Regulations on Implementing the Law of the People's Republic of China on Countering Foreign Sanctions[1] (Order of the State Council No. 803) (hereinafter referred to as the “Regulations”).
The Regulations provide detailed rules for implementing the Law of the People's Republic of China on Countering Foreign Sanctions (hereinafter referred to as “Law on Countering Foreign Sanctions”) with an aim to strengthen the legal framework of countermeasures to foreign sanctions.
1.Application Scope of the Countermeasures
The Regulations provide that entities may be added to the anti-sanctions list and subject to countermeasures under the two following circumstances.
· If any foreign country violates international law and basic norms governing international relations by using any excuses or its domestic laws to contain and suppress China, to impose discriminatory restrictive measures on Chinese citizens or organizations, or to interfere in China's internal affairs, or
· if any foreign country, organization, or individual implements, assists or supports actions that harm China's sovereignty, security, or development interests.
Compared with the provisions of the Law on Countering Foreign Sanctions, the Regulations expand the application of the anti-sanctions list and countermeasures to any foreign organization or individual that “assists or supports” the actions that harm China's sovereignty, security, or development interests, as well as their “associated organizations and individuals”. However, the Regulations do not further clarify the definitions of the foregoing terms and scope of “discriminatory restrictive measures”.
2.Specific Measures and Working Mechanism
The Regulations develop a coordinated working mechanism consisting of the foreign affairs, commerce, development and reform, judicial administration and other authorities under the State Council for implementing the anti-sanctions list and countermeasures. In addition, the Regulations explicitly require the relevant authorities under the State Council to enhance collaboration and information sharing in the determination and implementation of countermeasures. [2]
In Articles 6 to 9, the Regulations further set forth the enforcement authorities responsible for each specific countermeasure, including the following.
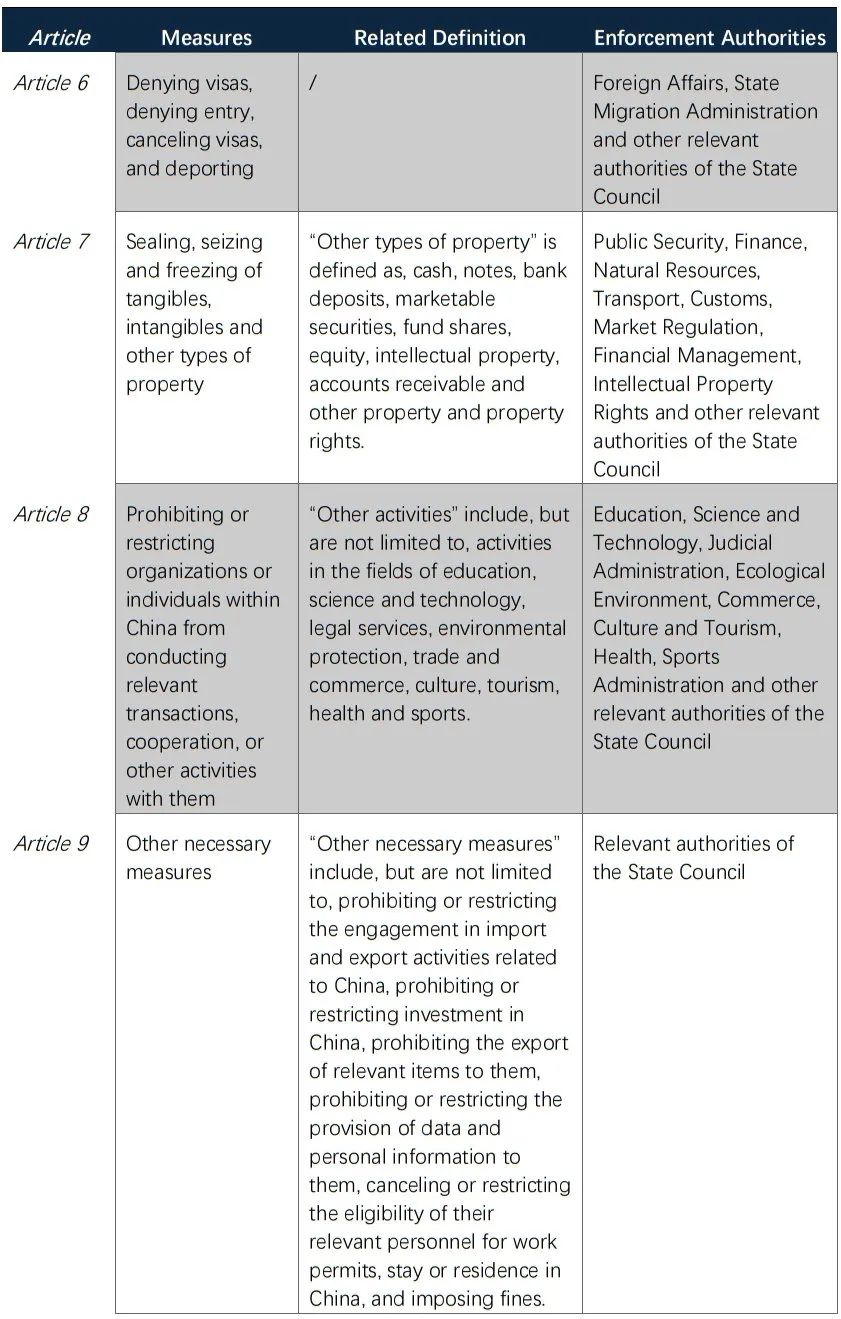
It is worth noting that, concerning the “other necessary measures” defined in Article 9 of the Regulations, in addition to those measures specifically provided in the Law on Countering Foreign Sanctions[3], the Regulations further incorporate other measures that have been put into use under other rules, such as the prohibitions and restrictions on import and export activities and investment in China under the Provisions on the Unreliable Entities List. Moreover, the Regulations, for the first time, adopt prohibition and restriction on the provision of data and personal information as one of the enforcement tools.
3.Legal Liabilities
(1)Legal liabilities concerning failure to comply with the countermeasures
Pursuant to Article 13 of the Regulations, entities that fail to comply with the countermeasures may be ordered to make corrections, be prohibited or restricted from participating in government procurement, bidding and tendering, or from the import and export of relevant goods and technologies or international trade in services, be prohibited or restricted from receiving or providing data or personal information from or to foreign countries, and be prohibited or restricted from leaving the country or from staying and residing in China, etc.
(2)Legal liabilities concerning implementing or assisting in implementing the discriminatory restrictive measures
On the basis of Article 12 of the Law on Countering Foreign Sanction, Article 17 of the Regulations further provides specific requirements regarding the prohibition on any organization and individual (including Chinese and non-Chinese entities) from implementing or assisting in the implementation of the discriminatory restrictive measures taken by any foreign country against any Chinese citizen or organization. Failure to comply with this prohibition will result in not only administrative measures including regulatory talks, orders of corrections and appropriate measures, but also potential civil litigation.
In this regard, Article 18 of the Regulations further grants Chinese citizens and organizations the right to file lawsuits against organizations and individuals that implement or assist in the implementation of discriminatory restrictive measures, which infringes on the legitimate rights and interests of Chinese citizens and organizations.
In fact, Article 12 of the Law on Countering Foreign Sanction has already been referenced as a cause of action in court decisions in China. In a dispute over tort liability between an offshore engineering company and S Equipment Company[4], an offshore engineering company (hereinafter referred to as the “Plaintiff”) was placed on the sanction list by a foreign country, based on which the S Equipment Company (hereinafter referred to as the “Defendant”) suspended the payment of the final instalment of US$11.86 million on the grounds of executing an administrative order of the third country. The plaintiff filed a lawsuit with the Nanjing Maritime Court pursuant to Article 12 of the Law on Countering Foreign Sanctions. After the defendant applied for a payment license from the third country, the Plaintiff and the Defendant eventually reached a mediation agreement.
(3)Legal liabilities concerning interference with national sovereignty through litigation
Article 19 of the Regulations further provides, if any foreign countries, organizations, or individuals harm China's sovereignty, security, or development interests through promoting or implementing litigation or other means, the relevant authorities shall have the authority to decide to add such entities and their associated organizations and individuals involved in such litigation, enforcement of judgments, or other activities in the anti-sanctions list, as well as to impose countermeasures such as restricting entry, sealing, seizing, freezing their property within China, and prohibiting or restricting relevant transactions or cooperation with them, while reserving the right to enforce against their property and impose other more severe countermeasures.
In addition, no organization or individual shall implement or assist in implementing judgments resulting from litigation promoted or implemented by foreign countries, organizations, or individuals.
4.Procedural Requirements on Implementing the Countermeasures
(1)Requirements on transparency
The Regulations emphasize the rules of information disclosure and transparency. When the relevant authorities of the State Council make decisions on the determination of countermeasures, they are required to make clear the application scope of the countermeasures, the specific countermeasures, and the date of implementation[5]. In addition, when the relevant authorities decide to impose, suspend, amend, or cancel any countermeasures, they are also required to publish and update the information through their official websites and other relevant channels[6].
(2)Petitions for suspension, amendment, or cancellation of the countermeasures
After a decision to impose countermeasures is announced, an organization or individual subject to the countermeasures may apply to the relevant authorities that made the decision for suspension, amendment, or cancellation of the countermeasures[7]. The relevant authorities that made the decision to impose countermeasures are also authorized to organize an assessment of the implementation and effectiveness of the countermeasures. Based on the assessment results or the review of the application submitted by an organization or individual subject to the countermeasures, the relevant authorities may suspend, amend, or cancel the countermeasures. [8]
(3)Applications for approval
For those entities that need to engage in prohibited or restricted activities with an organization or individual subject to the countermeasures due to special circumstances, applications are required to be submitted to the relevant State Council authorities for approval.[9]
Compliance Advise
The Regulations are a powerful supplement to China's legal framework of anti-sanctions list and countermeasures. In line with the core principles of the Law on Countering Foreign Sanctions, the Regulations refine the procedural and substantive requirements, and provide clearer compliance guidance and remedial measures for relevant market participants.
We suggest all foreign companies and their Chinese subsidiaries taking the following actions.
(1) Closely monitor the developments and updates to the Chinese sanction policies, countermeasure lists and countermeasures.
(2) Develop and improve internal compliance programs based on the legal requirements and obligations under the Law on Countering Foreign Sanctions and the Regulations and implement them in daily operations. Update and modify the relevant Sanction Compliance clauses in transaction documents accordingly.
(3) Prohibit participation in litigation that may endanger China's national sovereignty, security and development interests, and refrain from enforcing the court rulings in China made through such litigation.
(4) Seek assistance from both foreign and Chinese counsel if there is a need for filing lawsuits when facing the conflict of laws or sanctions dilemma.
[Note]


Guoxun Zhang
Beijing Office
Senior Counsel

Practices:Trade Compliance & Trade Remedies, Antitrust & Competition, Customs & Import/Export
Industry Sectors:Telecommunications & Internet, Information & Intelligence Technology

Zhiguo Yu
Beijing Office
Non-equity Partner

Practices:Trade Compliance & Trade Remedies

Jenny Pan
Beijing Office
Regulaotry Compliance Dept

Tristan Zhang
Beijing Office
Regulaotry Compliance Dept

《Navigating PRC's Foreign Relations Law: Principles & Compliance》
《Law and Enforcement of China's Export Control and Sanction 2023》
《Scope Ruling in China AD Investigation: Implications for Brandy》
《Navigating PRC's Foreign Relations Law: Principles & Compliance》
特别声明
以上所刊登的文章仅代表作者本人观点,不代表北京市中伦律师事务所或其律师出具的任何形式之法律意见或建议。
如需转载或引用该等文章的任何内容,请私信沟通授权事宜,并于转载时在文章开头处注明来源于公众号“中伦视界”及作者姓名。未经本所书面授权,不得转载或使用该等文章中的任何内容,含图片、影像等视听资料。如您有意就相关议题进一步交流或探讨,欢迎与本所联系。
















发表评论